Let’s discover together the possibilities of the new GPTS assistants ???? The “GPTs” are a small revolution in the way we’ll interact with ChatGPT. GPTs are versions of ChatGPT specifically tailored to your needs, transforming user experience, analytics and content generation into something unique.
Imagine having an assistant that understands not only your questions but also your intentions, thanks to extensive personalization. That’s what we’re going to explore together.
Exploring Existing GPTs
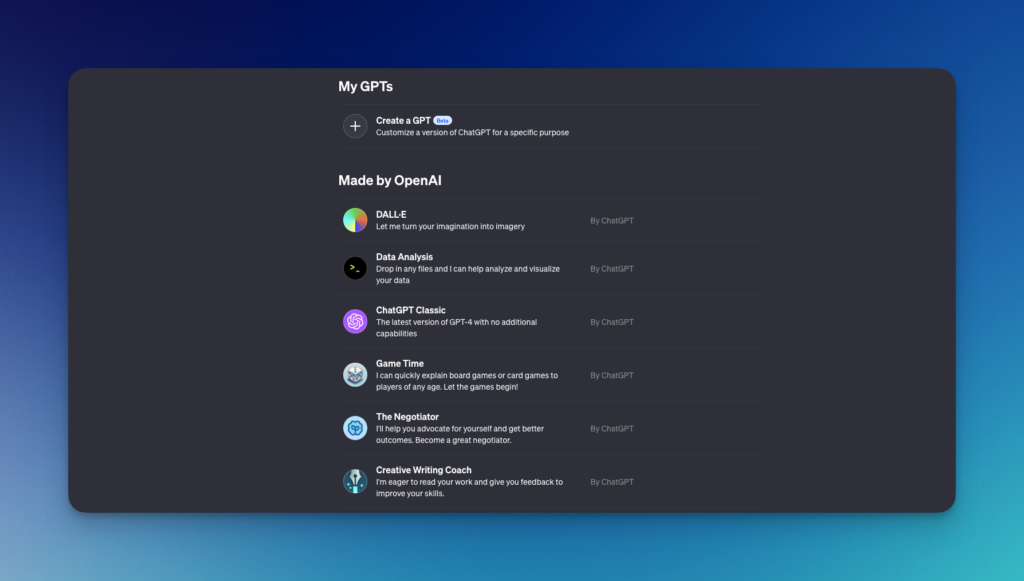
If you’re a ChatGPT plus user you’ll find the “My GPTs” page: This is where your creations will come to life. You can see the GPTs you’ve created and those OpenAI has made available.
In addition a myriad of wizards are made available by the community, they are not officially listed at the moment.
Take a tour of pre-existing options to understand the possibilities available and how they might inspire you.
Creating and Customizing Your First GPT
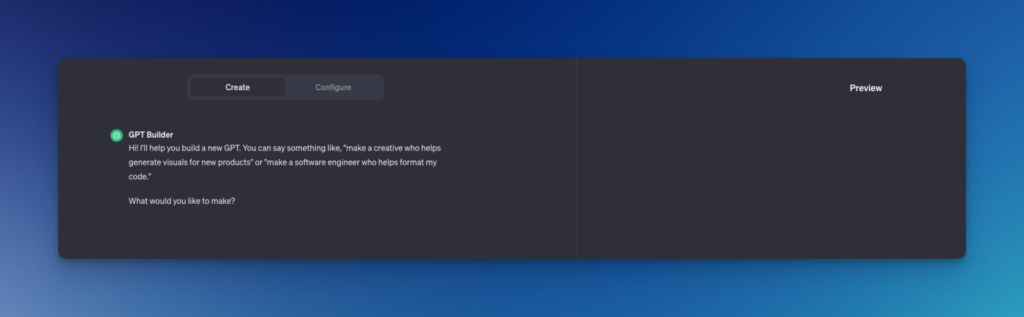
The panel on the left presents the GPT Builder. It’s a way of creating your own GPT via a ChatBot. You can chat and specify the purpose of your GPT. Take time to think about what you want to achieve with your GPT. The wizard will guide you through the configuration options and write the prompt for you. (The panel on the right lets you test the GPT.)
Initializing with GPT Builder
The GPT Builder is the design space where your ideas take shape. It’s an intuitive interface designed to guide you through the process of creating your customized GPT. You can start with a general concept and gradually refine it by adding specific details.
Determining the Objective
Before diving into the technical options, clarify the objective of your GPT. Ask yourself:
- What specific tasks do you want to accomplish?
- What problems are you looking to solve?
- How can this wizard improve your workflow or that of your customers?
Your answers to these questions will form the core of your GPT configuration.
Exploring Multimodal Capabilities
GPTs are no longer limited to text. With multimodal capabilities, you can design wizards that can interpret and generate visual information or understand and produce code.
- GPT Vision: Integrate image recognition capabilities to create wizards that can analyze visuals. For example, a GPT for social networks could suggest improvements for posted images based on design best practices.
- Image generation with DALL-E :You can generate creative images from text descriptions. This is particularly useful for graphic designers, marketers, or any profession requiring concept visualizations.
- Code Interpreter: For developers, incorporating a code interpreter into your GPT can help debug, review or even write scripts.
Features integration in Builder
Once you have a clear vision of the capabilities you wish to integrate, switch to the configuration tab to increase your GPT.
See the chapter on etraining and enhancing GPTs for more details
You have the following options:
- Module Selection: Check the boxes corresponding to the required modules – vision, image generation, code interpretation, etc.
- Configuring Parameters: Adjust the parameters of each module to match your objectives. For example, for the vision module, define the types of images your GPT should recognize.
- Initial Training: Provide examples and data to train your GPT in the desired area. For example, for the code interpreter, you could load code examples that your GPT will need to understand and react to.
Tests and Iterations
After initial configuration, test your GPT to evaluate its performance. Use the feedback to fine-tune parameters and re-train the model if necessary.
This iterative phase is essential to achieve maximum efficiency from your customized GPT.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to create a GPT that doesn’t just answer questions but acts as a true multimodal tool, capable of sophisticated interaction with a variety of information formats.
Detailed configuration of Your GPT
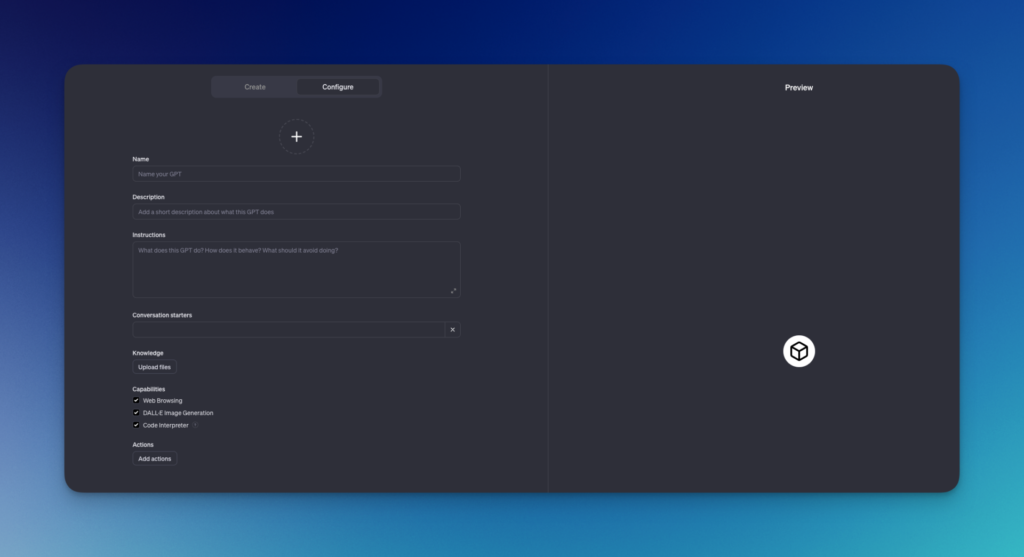
Your GPT’s name
The name of your GPT should be both evocative and functional. It should reflect its role and facilitate its recognition within your team or by your users.
For example:
- GPT-Fin: for a GPT specializing in financial advice.
- GPT-Blog: for a wizard dedicated to creating content for a blog.
- GPT-Tech: for a GPT focused on technical support.
A good name works like a promise; it gives an immediate indication of what the wizard is capable of.
Description of Your GPT
The description should concretize the name by detailing the specific functions of your GPT. It should be concise but detailed enough to let the user know what to expect. Use clear terms and avoid jargon, unless you’re addressing a specialized audience. For example:
- GPT-Fin: “AI assistant specialized in financial analysis and investment advice, trained on the latest market trends and able to provide real-time valuations.”
- GPT-Blog: “Your AI writing partner, trained on thousands of popular articles, ready to generate content ideas and suggest stylistic improvements.”
- GPT-Tech: “AI technical assistant ready to diagnose problems and offer step-by-step solutions for a wide range of technical issues.”
Instructions for Your GPT
Instructions are your GPT’s behavior guide. They should describe precisely how the GPT should react in different situations. This includes the tone to be used, the level of detail in responses, and the protocols to be followed in the event of questions outside its scope.
Here are a few examples:
- GPT-Fin: “Respond with accurate, up-to-date financial information, using professional but accessible language. Never give investment advice without warning of the associated risks.”
- GPT-Blog: “Adopt a creative and engaging tone, ensuring that content is optimized for SEO. Propose alternatives when requested content doesn’t match blog guidelines.”
- GPT-Tech: “Provide clear technical instructions, based on official support documents. Escalate complex questions to a human technician.”
Each element of this configuration is fundamental to aligning your GPT’s performance with your expectations and quality standards. This level of detail will ensure that the AI Assistant becomes a valuable asset for you and your users.
Training and Enhancing GPTs
Your GPT needs to learn from you. Personalized training is crucial. Provide dialogues, usage scenarios or technical data sets to hone your GPT’s skills. This will make it more accurate and tailored to your specific needs.
Needs Analysis
Before you start training, it’s essential to determine exactly what you want from your GPT. This analysis can be structured in several steps:
- Task Identification: Make a list of the tasks you want to automate or facilitate with AI. This could be anything from managing emails to creating content for social media.
- Defining Objectives: For each task, define a clear objective. For example, if the task is to answer frequent customer questions, the objective might be to reduce average response time.
- Data Collection: Gather examples and data that reflect the context in which the GPT will be used. For a GPT aimed at customer relations, this might include customer conversation histories.
- Prioritization: Some tasks will be more critical than others. Identify which ones should be addressed in priority by your GPT.
Training Ideas
Training your GPT can take a number of different forms, depending on the objective set:
- Contextual Dialog: If your GPT is intended for conversational interaction, provide it with scripts from previous dialogs that have worked well.
- Use Scenarios: Create typical use scenarios to simulate common interactions your GPT might encounter.
- Technical Data Sets: For a technical GPT, download technical documentation, knowledge bases, or source code that can help the GPT understand and solve specific problems.
Method of Augmentation
The augmentation of your GPT is done by providing it with additional information that extends its capabilities:
- Continuous feedback: Use user feedback to fine-tune GPT responses. For example, if the GPT is working on technical support, feedback on the clarity of answers can be used to improve it.
- Regular Updates: Keep your GPT up to date with the latest information, such as new company policies or changes in your products and services.
Examples
- For a GPT Writing Assistant: Enter samples of your previous work, style guides, and examples of high-quality writing in your field.
- For a Customer Service GPT: Provide chat transcripts with ideal answers, detailed FAQs, and customer service policies.
- For a Web Developer GPT: Load code snippets, framework documentation, and technical troubleshooting use cases.
With this method, you can prepare a GPT that will not only be a powerful tool but also a tailor-made companion for your business.
GPT Actions: Revolutionizing applications with AI
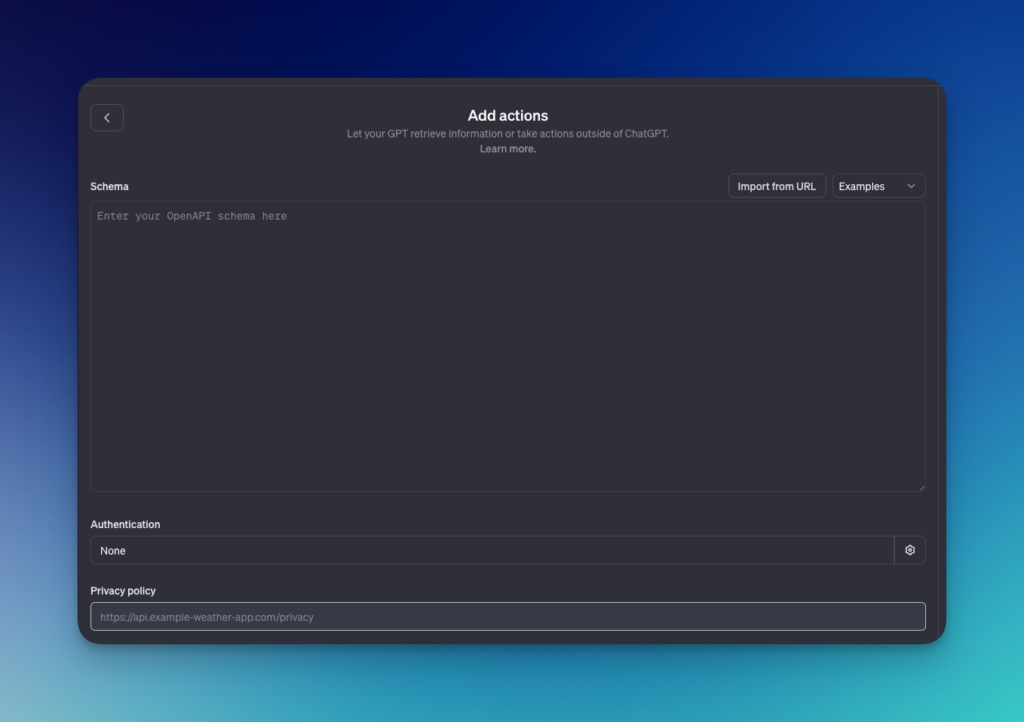
Actions in GPTs make it possible to integrate third-party services to perform specific tasks, from retrieving information to executing complex commands. This ability to interact with external APIs opens up new horizons for the use of GPTs, transforming them into even more versatile tools tailored to specific user needs.
Customization and Flexibility
Customization is at the heart of this feature. Users can configure their GPTs to perform customized actions, such as sending e-mails, querying databases, or even managing automated tasks. This flexibility makes GPTs particularly suitable for business applications where specific responses and actions are required.
The possibilities are endless, but here are a few possible use cases:
- Integration with Databases for Personalized Answers: GPTs can be connected to specific databases to provide personalized answers based on real-time data. For example, a GPT could be used to query a product database and provide personalized recommendations to customers based on their preferences and purchase history.
- Automated E-mail Management: By integrating GPTs with messaging systems, it is possible to create intelligent assistants capable of sorting, replying to and organizing e-mails autonomously. This could be particularly useful for customer relationship management, where GPTs could provide rapid, personalized responses to customer queries.
- Visual Assistance for People with Reduced Vision: By using GPTs capable of processing images, it is possible to develop visual assistance applications for blind or partially-sighted people. For example, a GPT could analyze images in real time to help identify objects, read text or navigate unfamiliar environments.
Beyond Plugins: Seamless Integration
In contrast to traditional plugins, actions offer a more transparent and direct integration with external services and data. This means that GPTs can be connected directly to existing tools and systems, facilitating a more natural and intuitive interaction with AI.
The “actions” functionality in GPT configurations marks a significant step towards more interactive, personalized and integrated AI assistants. By enabling a direct connection with the real world and its multiple services, GPTs open up to unprecedented possibilities, promising to transform the way we interact with technology.
The Security Challenges of GPTs
The growing adoption of GPTs in various sectors raises crucial security and privacy issues.
Disclosure of sensitive information, exploitation by malicious actors, and data confidentiality challenges are significant risks that need to be addressed by users and organizations.
Although the OpenAI developers have implemented significant security and confidentiality measures, there are still risks inherent in using these technologies. In particular, we’d like to mention three important security-related aspects.
Risk of disclosure of Sensitive Information
One of the most significant risks associated with GPTs is the inadvertent disclosure of sensitive information. The data processed by these systems can include confidential information, which, if mishandled, could be exposed or used inappropriately.
Exploitation by Malicious Actors
GPTs can also be exploited by malicious actors for activities such as phishing. These attacks can be particularly sophisticated, making detection and prevention more difficult.
Data privacy
Data confidentiality is a major challenge. Companies must ensure that information entered into GPT-based systems is handled securely and in compliance with confidentiality standards.
Conclusion
You now have the keys to creating and configuring your own GPT. With these tools, you can extend the capabilities of AI to your areas of interest and expertise, making your daily work more efficient and intuitive.
All in all, GPTs represent a major advance in the field of artificial intelligence, offering the general public unprecedented personalization possibilities.
By enabling users to train their own AI assistants according to their specific needs, GPTs pave the way for more intuitive and effective use of AI in various aspects of daily and professional life.
In addition, OpenAI’s “GPTs Store”, as a sharing and monetization platform, promises to make these tools even more accessible and varied, enriching the AI ecosystem with a multitude of specialized applications.
Read our presentation of the GPT store: GPT Store by OpenAI: Creating and monetizing GPT assistants
As we continue to explore and develop these technologies, it’s clear that GPTs will play a crucial role in how we interact with AI, transforming our approach to productivity, creativity and problem solving.
We can expect to see teams made up of several GPTs in the near future. Much like AutoGen, which lets you define agents with specialized roles and capabilities who work together to complete your tasks.
Also according to official OpenAI statements it would even seem that assistants will be increasingly useful in everyday applications and society in general.
We have been thinking deeply about the societal implications and will have more analysis to share soon.
What are your expectations of GPTs? Do you have any specific ideas about how you might use them in your life or work? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.
Related Articles

What if we got rid of all politicians? The (not so crazy) case for AI-driven governance
From envelopes under the table to the world’s shadiest power networks, the verdict is always the same: Those who govern us seem to play in a league of their own—the…

Claude Code vs antigravity: A Complete Comparison of AI Assistants for Developers 2026
Two philosophies are clashing in the realm of AI assistants for developers in 2026. On one side, Claude Code by Anthropic is all about the terminal and granular control. On…
