
UX design is an exciting field, and some controversies can divide professionals when it comes to web design and particularly the choice of interactions and functionalities for a website.
Sometimes web design is so standardized that it conflicts with the user experience. In this article, we’ll discuss the interface elements that sometimes cause debate; Notably the modal windows or “pop-ins”, the hamburger menus, the header slideshows, the design “above the fold”, the infinite scroll as well as the sidebars of blogs.
We’ll look at the pros and cons and discuss best practices to help you decide whether these features are appropriate for your website.
Please note that this article is far from exhaustive, and we may delve further into certain points. The aim is simply to present a few essential web interactions and share our experiences and visions of web design.
So feel free to leave comments! 🙂
Modal windows or “pop-ins”
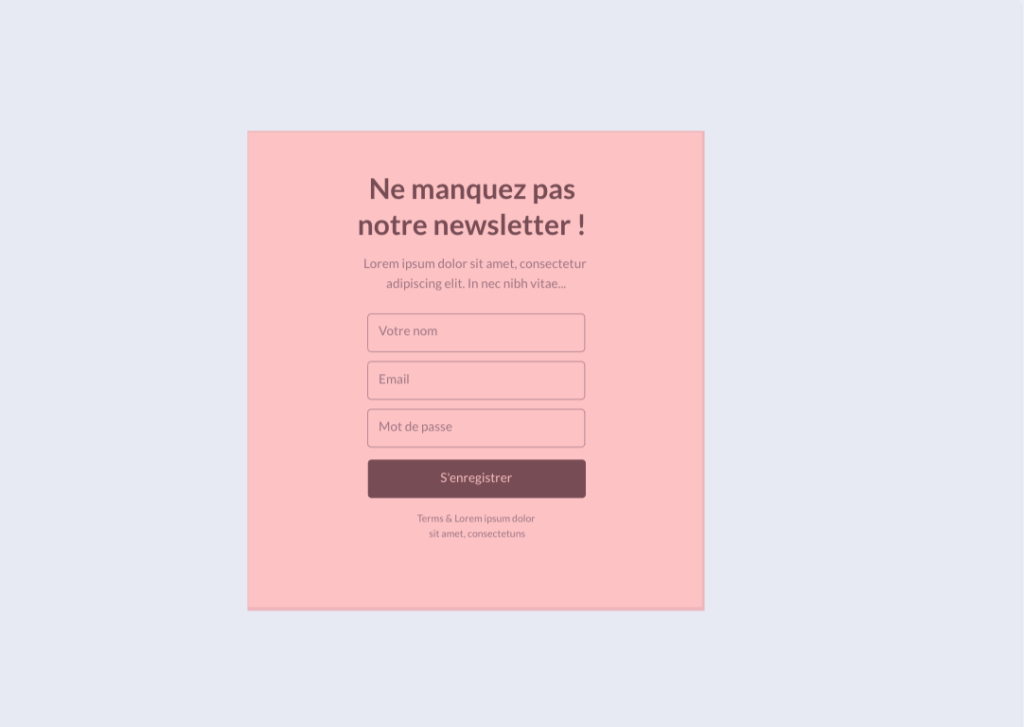
Always widely used on blogs and some storefront sites, pop-ins are pop-up windows that open on the user’s screen as they interact with the website. They can be used to display additional content, such as forms, ads or contact information. Their purpose is to retrieve information or engage visitors on an action.
Generally poorly designed, they are intrusive and counter-productive with regard to accessibility criteria, and from a UX point of view, these ads are perceived as unsolicited advertising.
So why set up these interactions? What are the drawbacks? What precautions should be taken when implementing them in a web design?
What are the advantages?
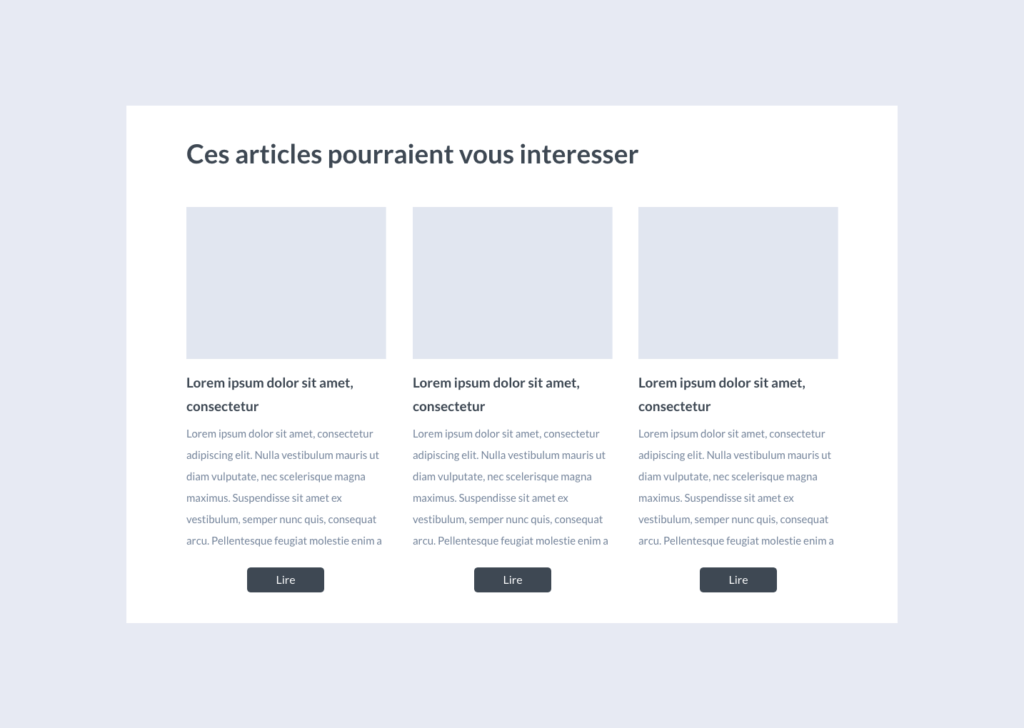
Generally speaking, the interest remains in increasing your site’s conversion rate. This may involve developing your e-mail base, promoting content or products. Pop-ins remain an interesting tool in the web-marketer’s panoply.
In fact, they can even enhance your site’s UX and complement the browsing experience under certain conditions. For example, by displaying a modal window that will suggest cross-navigation links or targeted content at the end of your reading.
Why give up on pop-ins?
In an effective marketing strategy, this technique can be useful on a website but remains very risky if the device isn’t properly implemented and configured.
From the user’s point of view, pop-ins are rarely desirable; unlike a dialog box, the spontaneous opening of a window when consulting a page will distract, at worst irritate, the user. It constitutes friction and may push the visitor to leave the site.
Before opting for this solution, keep the following points in mind:
- Pop-ins are similar to unsolicited advertising
- They short-circuit navigation
- They are often inefficient
- Google penalizes mobile sites with popups
How to make opt’in effective with pop-ins?
Pop-ins can harm a site and lower its conversion rate, unless they offer useful, relevant and contextualized content.
They’re mainly used to present special offers or important information in a way that won’t go unnoticed.
- Propose a contextualized promotion (online store)
- Propose high-value content relevant to your target audience (Ebooks / Downloads)
How best to integrate it into the browsing experience?
- Create visually original and targeted pop-ins
- Find teasers that clearly explain the interest for your users
- Find the right timing to trigger the modal window so as not to aggress visitors.
- Trigger display in “Exit intent” or on scroll or inactivity
- Do not display pop-in multiple times
Header slideshow
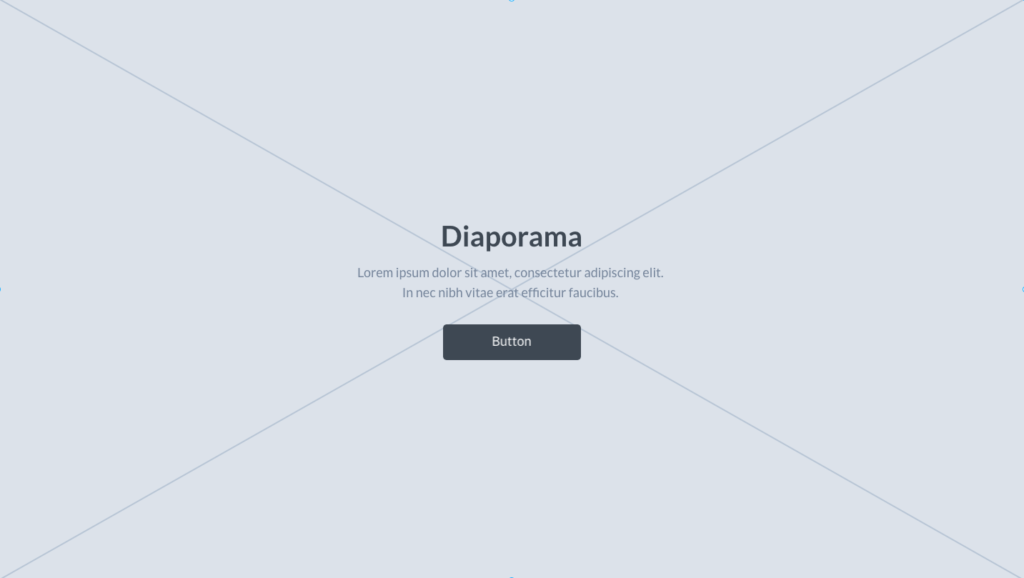
Slideshows have gradually become a standard in web page design, and have imposed themselves on interface designers.
Users are familiar with how they work, but is this a good thing? What are the real benefits of integrating a slider or carousel into a home page?
The original intention is to present a selection of content and create interaction, but in reality header slideshows generally don’t hold visitors’ attention, and the majority of content presented won’t be viewed.
What advantages can be found in header slideshows?
- Wow effect
- Present multiple images or messages in an attractive, visual way
- Generally easy to customize and update
- Offer the possibility of presenting dynamic and interactive content
Why avoid slideshows and what are the alternatives?
- Often all or part of the content presented is ignored
- May be slow to load and slow down page load time
- Sometimes distracting for users and alter the user journey
- May be difficult to use on mobile devices
Adding a horizontal dimension can disrupt the reading direction of the page, which most of the time is vertical. This leads to user distraction.
What alternatives can be considered to improve ergonomics and the user experience?
Instead of a slideshow, choose a still image that reinforces your message and your company’s image, it will have more impact on visitors because it will focus on the essentials. “Less is more”
Design “above the fold “
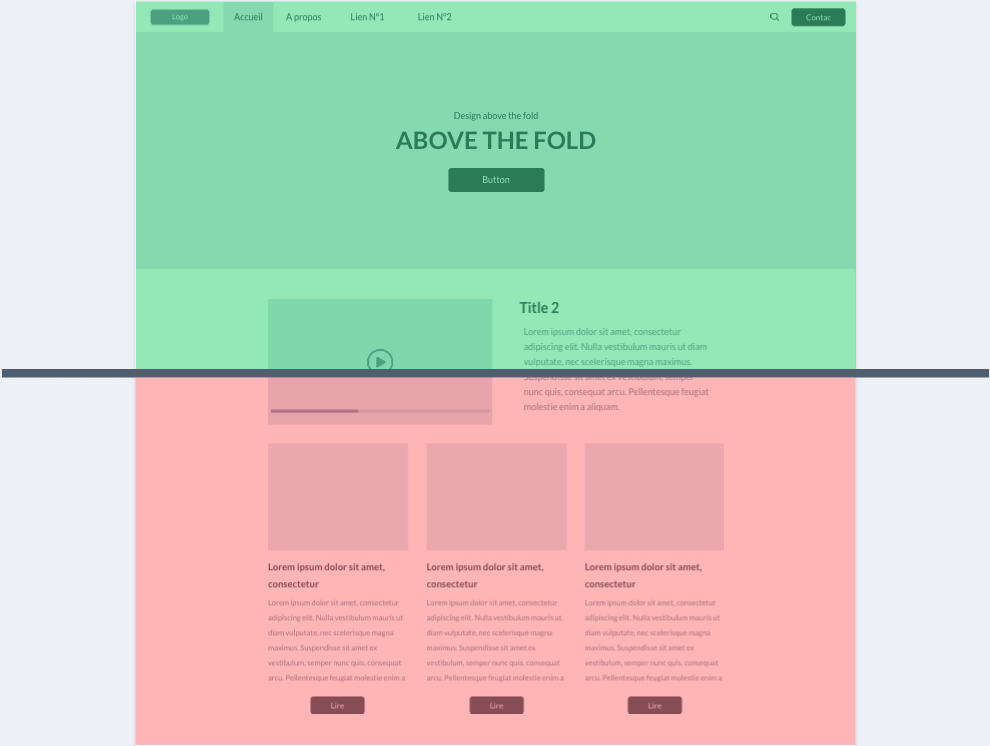
The above the fold design of a website corresponds to the part visible without scrolling the page and can be crucial for the user experience as it is the first impression you will give.
It’s therefore important to take care of this part of the page by strategically placing important elements and ensuring a clear, consistent layout.
What are the ergonomic constraints associated with this type of web design?
Space limitation
The space available at the top of the page is generally limited, which can make it difficult to integrate all the important elements. It may be necessary to make choices and prioritize information to avoid overloading this part of the page.
Risk of confusion
by presenting too many elements or information at the top of the page, there is a risk of confusion for users, who may not know what to look at first and not know how to navigate the site.
Uneven highlighting of elements
Depending on their position on the page, some elements may be highlighted more prominently than others, which may disadvantage certain content or functionality.
Poor experience on small screens
If the above-the-fold design is designed to be visible on large screens, it may be difficult to read or access on small screens, which can harm the user experience…
When designing try to strike a balance between presenting all the important information, readability and accessibility of the page.
Hamburger menus

“Hamburger” menus (or “three-bar menus”) are navigation menus that are usually presented as a button with three horizontal bars and reveal the site’s main menu when activated.
What are the advantages of using a “Hamburger” menu?
- Like a “home” or “trash” icon, the hamburger icon is recognizable by most users. It represents, in a simple way, access to the menu.
- It saves space on the interface. For mobile it’s a must, but some sites use it for desktop versions too
- It’s a well-known fact that presenting your users with too many choices is counterproductive. That’s why the Hamburger menu is interesting, as it avoids distraction by hiding navigation links.
Are there any Drawbacks to Hamburger menus?
Despite the advantages, there are still some accessibility issues.
- Longer discovery time: to find the main menu, users sometimes have to click on the “hamburger” button, which can be time-consuming and frustrating.
- Less visibility of navigation links: hiding the main menu, “hamburger” menus
- Unintuitive: For some users, “hamburger” menus can be unintuitive and they may not understand how to access the site’s main menu.
Should this be implemented?
Maybe it’s simply a matter of considering the importance of the pages contained in the menu. Indeed if these pages aren’t immediately useful to the user, perhaps it’s a good idea to prioritize their attention on content and the messages you want to get across. This is why the hamburger menu is also a good option for bringing together the site’s secondary pages.
In addition It is possible to overcome the accessibility of navigation links by creating calls to action on target areas of the page.
Infinite scroll
Infinite scroll is a content loading technique that loads new pages of content as the user scrolls through a website. Instead of loading all the content on a website at once, infinite scroll loads only the content that is visible on the user’s screen, and loads new pages of content as the user scrolls down the page.
What are the potential drawbacks of using infinite scroll on a website?
difficult navigation
Infinite scroll can make it difficult to navigate to a specific page or return to a previously visited page, as there are no clear navigation links to other content pages.
Longer loading times
Infinite scroll can lead to longer loading times for some sites, especially when there’s a lot of content to load.
Is infinite scrolling an ethical issue?
Although not considered a dark pattern per se, it can be abused to get users to spend more time on a site or consume more content. For example, an e-commerce site may use infinite scroll to hide filtering or sorting options, so that users have to browse through an unlimited number of products before finding what they’re looking for.
It’s important to note that infinite scroll can be useful in certain situations, such as when used to display large amounts of content consistently and efficiently. However, it’s important to ensure that this technique is used fairly and transparently, and that users can easily access filtering and sorting options if they wish.
Sidebar for article pages
The sidebar is the side column that appears on most blogs and can be used to present additional content, such as links, categories or ads.
Can it help you improve your blog’s user experience?
What are the advantages of a sidebar?
- It can help you organize your content in a coherent way and guide your users to other articles or categories that might interest them.
- It’s useful for improving navigation and content discovery on your blog.
What are the disadvantages of a sidebar?
- It can take up valuable screen space and distract users from the main content
- It can also be difficult to use on mobile devices, and can be too busy and detract from the readability of the main content.
- Finally, it may be unnecessary or disruptive for some users.
If you choose to integrate a sidebar into your web design, It’s important not to overload it with too many features and to keep it organized and easy to use for users.
To conclude, web design is a complex and controversial discipline, all the more so when it comes to UX issues. Many elements need to be taken into account to create optimal interfaces and user experience. Elements such as modal windows, header slideshows or sidebars can all be useful or harmful depending on how they are used.
Beyond standards and fads, it’s essential to consider the user experience holistically and not lose sight of the context in which your site or application will be used.
Always take a step back when creating your web design, as the elements and interactions that are the norm today, are not necessarily suited to your project.
Finally, don’t forget that web design is a constantly evolving field, and that it’s important to stay up to date on innovations, particularly in UX and UI.
